Automotive Batteries Are An Example Of Which Hazard Class
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
UNUSUAL FIRE AND EXPLOSION HAZARDS. Examples of 18650 cylindrical cells these are the most common consumer electronics lithium-ion cell form factor.

Dot Hazard Classes Hazmat University
3 Batteries as described in Sec.
Automotive batteries are an example of which hazard class. And international hazardous materials dangerous goods regulations and are subject to specific packaging marking labeling and shipping paper requirements. The two most important types of rechargeable battery are leadacid and alkaline. Superior capacity has driven the demand for these batteries in electronic devices such as laptops power tools cameras and cell phones.
A battery is a hazardous waste if it exhibits one or more of the characteristics identified in 40 CFR part 261 subpart C. Lithium ion and lithium metal cells and batteries are listed as Class 9 Miscellaneous hazardous materials in the US. Batteries wet filled with acid electric storage.
2739 that are not hazardous waste. An example of a battery pack that contains multiple cells in. There are two main classes of battery.
Containers may explode when heated. It ignites easily and can. Battery or Battery Core Lead Acid PG III UN2794 Batteries wet filled with acid 8 154 4G fiberboard box or a 4HG plastic container.
Batteries emit hydrogen gas which is flammable. For nickel-metal hydride batteries transported by modes other than vessel. 348 Corrosives Hazard Class 8 3481 Definition.
A few more terms are defined in the packing instructions at 49 CFR 173185. Lithium ion battery cells and small battery packs 8 to 10 cells are in wide consumer use today. Batteries dry sealed nos.
Battery recycling of automotive batteries reduces the need for resources required for the manufacture of new batteries diverts toxic lead from landfills and prevents the risk of improper disposal. Batteries nickel-metal hydride see Batteries dry sealed nos. Cells and batteries also must meet certain testing requirements contained in the United Nations Manual of Tests and.
In 2011 the Foundation conducted a hazard and use assessment of these batteries with a focus on developing. A corrosive is any liquid or solid that causes visible destruction or irreversible alteration in human skin tissue at the site of contact or a liquid that has a severe corrosion rate on steel. The battery must be secured against movement and the terminals protected from short circuit.
The electrolyte in a battery is corrosive and can burn skin or eyes eat holes in clothing or even etch a concrete floor. This page gives advice about how to reduce the risks of using rechargeable batteries. SPECIFIC HAZARDS IN CASE OF FIRE.
The Hazardous Material Regulations of the USDOTPHMSA define a lithium ion cell or battery and lithium metal cell or battery at 49 CFR 1718. The term corrosive includes all items commonly referred to as acids as well as most batteries. Example of a hard case prismatic cell.
1 A used battery becomes a waste on the date it. Place the marking Batteries wet filled with acid UN2794 and the Hazard Class 8 label on the outside of the. Batteries evolve flammable hydrogen gas during charging and may increase fire risk in poorly ventilated areas near sparks excessive heat or open flames.
If the levels of hazardous substances or POPs are over a. Thermal shock may cause battery case to crack open. Those that can be recharged and those that cannot.
C Generation of waste batteries. Example of a soft-pouch polymer cell. Activated glass and screen phosphors.
There are four main hazards associated with batteries. Once a leadacid battery ceases to hold a charge it is deemed a used lead-acid battery ULAB which is classified as hazardous waste under the Basel Convention. Batteries dry containing potassium hydroxide solid electric storage.
Leadacid batteries are the most common large-capacity rechargeable batteries.

Hazard Class 101 Know How To Categorize Your Hazardous Materials

Top 10 Hazardous Materials From Labelmaster

Shipping Hazardous Materials Guide To Hazmat Shipping Shipbob
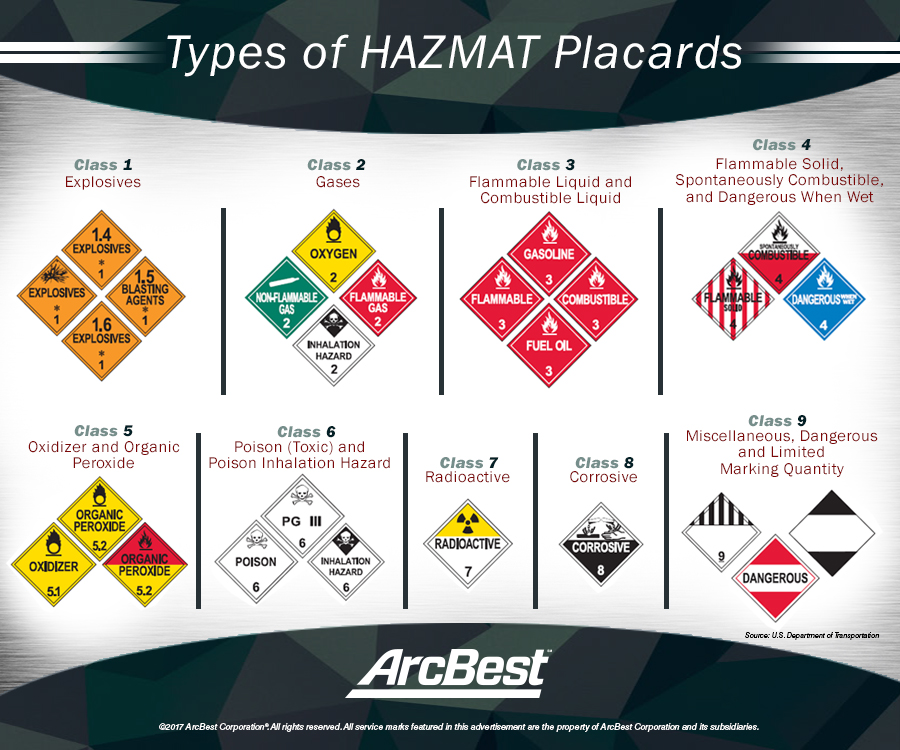
Understanding Hazmat Placards Arcbest
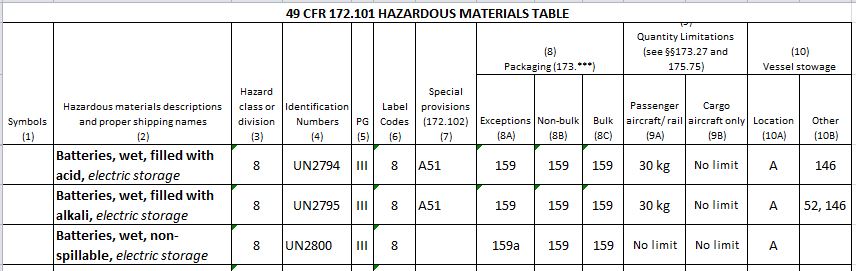
Packaging Wet Batteries For Transportation 49 Cfr 173 159 Daniels Training Services
Hazard Class 101 Know How To Categorize Your Hazardous Materials
Hazmat Placards And Un Numbers What You Need To Know Saferack

Hazardous Cargo Freight And Global Transport

9 Classes Of Dangerous Goods Hazardous Materials Dangerous Goods Classes Shippo
Hazard Class 101 Know How To Categorize Your Hazardous Materials
Distinguishing Dangerous Goods Hazard Class 9
2 Overview Of Hazardous Materials Transportation Cooperative Research For Hazardous Materials Transportation Defining The Need Converging On Solutions Special Report 283 The National Academies Press
Hazard Class 101 Know How To Categorize Your Hazardous Materials
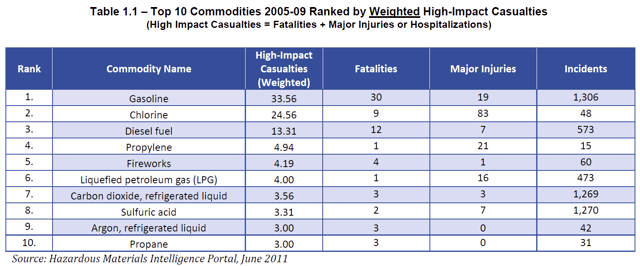
Top 10 Hazardous Materials From Labelmaster

Hazardous Cargo Freight And Global Transport
Hazard Class 101 Know How To Categorize Your Hazardous Materials

Hazmat Class Label Materials Labelmaster From Labelmaster
Distinguishing Dangerous Goods Hazard Class 8

Comments
Post a Comment